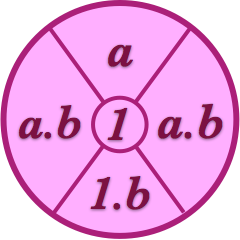The Knot System Explained
Here are more elaborate explanations of some of the components of the Knot System as defined on this page, including examples.
Ascent list n
The list of individuals in ascent list n is calculated by successively dividing n by 2 and discarding all fractions until 1 is reached. The list includes both the person (called person A in this example) and the ancestor n. For instance, person A's ascent list 13 is composed of the following persons:
- Ancestor 13 (whose number is halved to create 6.5; the fraction is dropped)
- Ancestor 6 (whose number is halved to create 3)
- Ancestor 3 (whose number is halved to create 1.5; the fraction is dropped)
- Person A 1
This means that A's ascent list 13 consists of four individuals: A him- or herself (n = 1), A's mother (n = 3), the mother's father (n = 6), and the mother's father's mother (n = 13). A's gender is unspecified. For the remaining individuals on the list, the gender is defined by the ancestor position number as previously stated, even numbers represent males, odd, females. Therefore, A's ascent list n is an exact description of A's blood relationship to the ancestor at position n.
KinCode element
The most complex of the three basic relationships - i.e. the relationship between A and B, who have a common ancestor C - can be simply defined. One ascent list is compiled for A, beginning with him or her and ending with C. A second ascent list is compiled for B, beginning with him or her and ending with C. The resulting list number for A is linked to the resulting list number for B, by use of a decimal point - a.b being the manner of expressing this basic relationship, a KinCode element.
For all practical purposes, the KinCode elements may be treated as real numbers capable of being compared and sorted - as long as one precaution is observed. For all KinCode elements that have identical numbers to the left of the decimal point, the expressions to the right of the decimal point should all have the same number of digits. (Zeroes should be added to the right hand number to achieve this, but any added zeroes must appear immediately after the decimal point. Experience has proved it practical, always, to have at least two digits to the right of the decimal point. This permits the ascent list to span more than five generations and thereby accommodate most known descendant relationships.
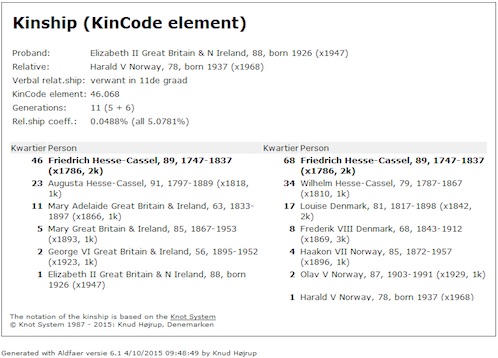
Below an example of how the genealogy program Aldfaer illustrates an expanded KinCode element 46.068 of the kinship between Queen Elizabeth II of Great Britain and King Harald V of Norway:
KinCode
One KinCode element is an exact description of a relationship when there exists only one knot individual between the Proband and the relative. This is however not always the case, for instance full siblings of the Proband will have both the father and the mother as common ancestors, two situations that fulfill the Knot individual definition.
Thus, in order to describe exactly a full sibling's relationship to the proband, two KinCode elements are needed one with the father as the knot individual (2.02), and one with the mother as the knot individual (3.03). The second element (3.03), is considered the mate element to the first, following the definition of the primary and secondary KinCode.
In some instances, there may be several knot individuals linking a proband with another specific relative. A knot individual can even appear in more than one ancestral position on both the proband's pedigree chart and that of the relative.
In order to describe fully the kinship in these cases, a separate KinCode element is required for each of this ancestor's positions and all combinations of them. The Knot individual definition though, must be fulfilled for all resulting elements. The related individual's KinCode will include all known KinCode elements.
In human genealogy, a verbal notation such as brother, sister, cousin, uncle, etc., is used to describe the closest
known relationship between two persons. The words of this notation are often accompanied by either full
or
half
to indicate whether the common ancestry comprises a couple or a single person. This closest relationship
is what the Knot System expresses in the primary KinCode.
Complex relationships
A complex kinship is illustrated in below screenshot, which shows the blood relations between Queen Elizabeth II of Great Britain and King Harald V of Norway, the Queen being the Proband. Her Kin group is constrained to a five-generation ascent and a six-generation descent. Within this scope, there are fourteen KinCode elements that specify exactly the relationship between Queen Elizabeth and King Harald.
The Knot individual, Prince Friedrich von Hessen-Kassel, appears only once in Queen Elizabeth's pedigree chart (at position 46), but three times in King Harald's pedigree chart (at positions 68, 92, and 116). Thus, there are three corresponding KinCode elements in King Harald's KinCode. The KinCode element screenshot above shows one of these elements, 46.068, expanded to show all individuals constituting that basic relation between the two monarchs.
To facillitate verification of this complex relationship pedigree charts for Queen Elizabeth II and King Harald V
may be downloaded here:
- Queen Elisabeth II of Great Britain (98 Kb).
- King Harald V of Norway (98 Kb).
Very complex relationship
An even more complex relationship exists between Queen Margrethe II of Denmark and Princess Marie Cécili of Prussia, it is documented here.
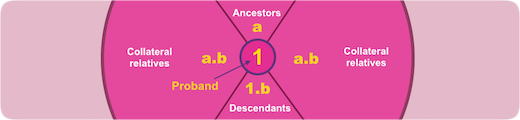
Kin group
Below a graphical illustration of a Kin group with the Proband, KinCode 1 in the center, the ancestors with KinCode's a in the upper sector, the descendants with KinCode's 1.b in the lower sector and collateral relatives (ancestor's descendants) with KinCode's in the form a.b in two sectors to the left and right.
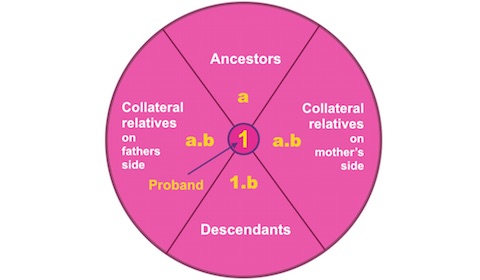
A Kin group may be constrained in size either by specifying a maximun number of generations distance from the Proband or by specifying the maximum number of ancestor generations and the maximum number of descendant generations.
A document showing a Kin group containing 3 ancestor generations and 3 descendant generations with all existing
relationship types may be downloaded here. Every relationship
type is exactly described with words together with the commonly used English Verbal relationship
notation.
Kin register
When members of a kin group are sorted in ascending numerical order on their primary KinCode, the resulting sequence shows a very interesting pattern. The first individual will be the proband (primary KinCode = 1), followed by the proband's own descendants generation by generation.
The descendants are followed by the proband's father and his descendants, one generation after the other. This set is followed by the mother and any descendants she may have by a mate other than the proband's father. This pattern continues through the generations of ancestors and their descendants for all members of the kin group.
The Kin register sequence of individuals resembles very much relationship patterns expressed in ancient laws for inheriting property and titles. When an individual (the Proband) dies, the children are the prime heirs. If those children are dead, their descendants, one generation after the other, will inherit.
If all descendants of the proband are extinct, the proband's parents and their descendants are next in the line of inheritance. If they are deceased too, the proband's grandparents and their descendants come next in the line - and so on until proper heirs are found.
Below screenshot shows how Aldfaer displays a Kin register for Queen Elizabeth II of Great Britain.